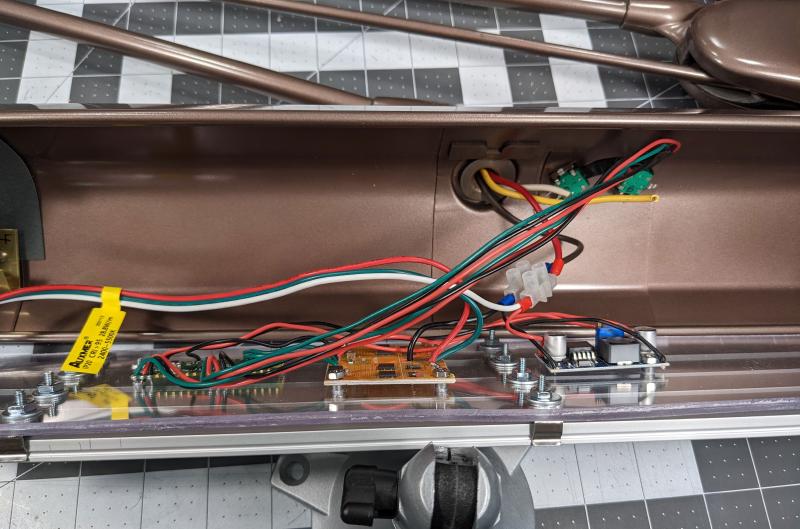
I recently completed a LED conversion on a Dazor P-2134 fluorescent tube task lamp.
Dazor has been making variations of this lamp since 1938.
The newly converted lamp has adjustable brightness and color temperature and uses a 20kHz PWM frequency to avoid any image banding on digital camera image capture.
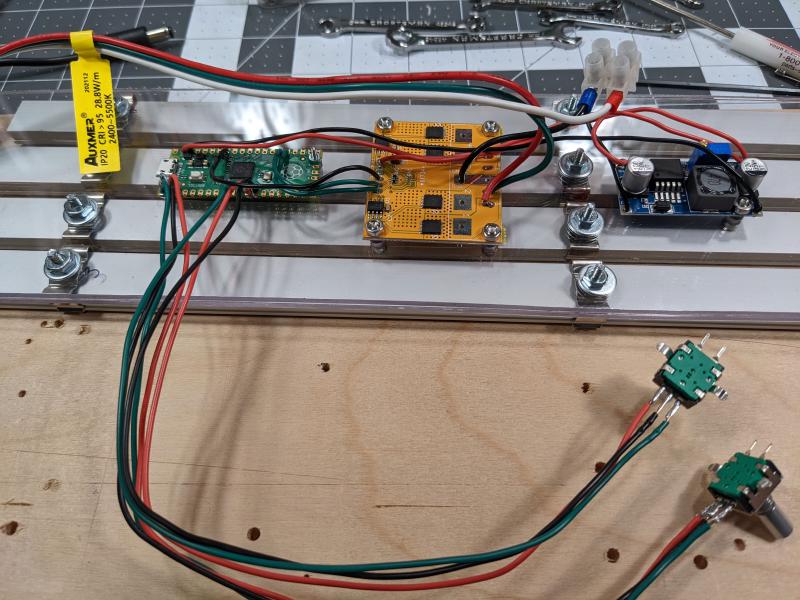
Here’s a list of the main components that I used for the conversion:
- Raspberry Pi Pico SC0915
- 4-Channel MOSFET board DMT10H010LPS (100Vds, 4.5Vgs) with gate driver option
- LM2596 DC-DC Buck Converter
- Auxmer 2400K + 5500K dual color temperature LED strip, 24V, 28.8W/meter, 120LEDs/meter, 95CRI aliexpress link use link at your own risk
- Muzata LED Aluminum channel with diffuser. I’d probably look for something better next time.
- Polycarbonate sheet to mount the LED channels and PCBs to
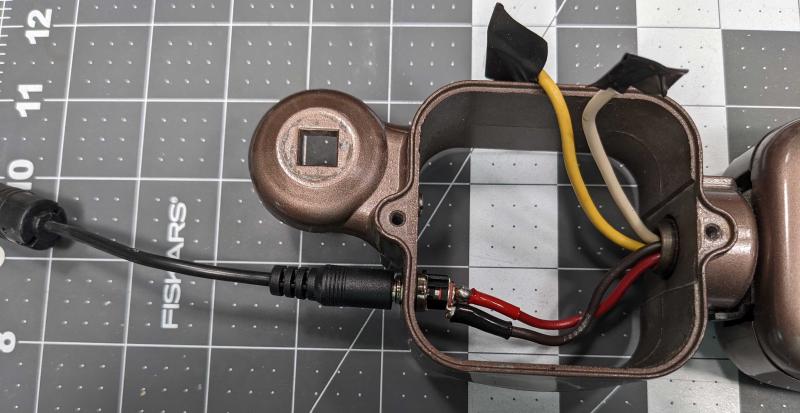
- Power jack 2.1X5.5MM EJ501A
- Rotary Encoders PEC11R-4215F-S0024. If I was doing this again I would look for ones with slightly longer threaded collars and shafts. I also ended up not using the push button switch
- Mean Well 24V 60W power adapter GST60A24-P1J. Maximum power draw is around 24 watts so this is overkill.
High frequency PWM dimming is needed to avoid image distortion on rolling shutter CMOS image sensors. A more detailed description of the problem is outlined in this article. The exact minimum frequency needed to eliminate this problem is dependent on the shutter speed and frame rate. Additionally to avoid any audible hum from the PWM switching you want to use frequencies above 20kHz.
The product guide for the 4-Channel MOSFET board by Spence Konde was helpful in getting everything wired up. I did make a hand drawn wiring sketch for this project and can provide it if anyone’s interested.
I’m running CircuitPython on the Pico and put together the code below for the lamp.
|
|